

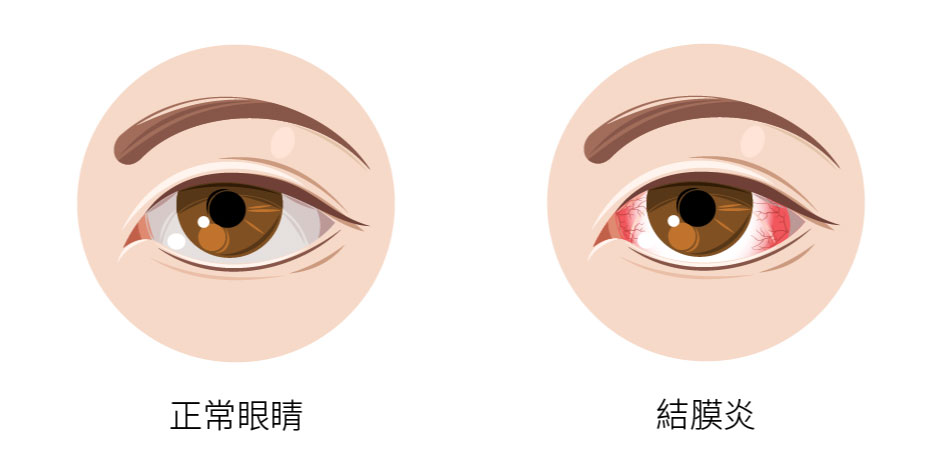
Conjunctivitis ( Pink eye)
Conjunctivitis (commonly known as pinkeye) is an inflammation of the transparent film covering the inside of the eyelids (the white part of the eye) and the surface of the eyeball.Iritis- refers to inflammation of the eyeball, and the places where the inflammation occurs are different.Conjunctiva- it lies on the outermost surface, the conjunctiva is easily affected by external factors and can become inflamed. Conjunctivitis has several causes, including infectious and allergic types. It may occur when the eye is infected by viruses or bacteria, or reacts to allergens and irritants such as pollen, secondhand smoke, chlorine in swimming pool water, cosmetic ingredients, or contact lenses. After infection, uncomfortable symptoms may appear, such as itching or stinging, redness, or a burning sensation in the eyes. Continue reading to learn more about the causes, symptoms, examination methods, and treatment options for conjunctivitis.
Causes of Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is the most common cause of red itchy eyes and is generally classified as allergic conjunctivitis or bacterial conjunctivitis.
Allergic conjunctivitis
Infectious conjunctivitis
Irritant conjunctivitis

Symptoms of Conjunctivitis
Discharge from the eyes
Itching or stinging eye
Redness in the eye and inner eyelid

Crusty eyelash and eyelid
Swollen eyelid

Burning sensation

More tears than usual
Management of Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is most commonly caused by viruses, bacteria, or allergies. If it is bacterial in origin, doctors may prescribe antibiotic eye drops to treat the infection. If it is viral, however, antibiotics are ineffective and may even reduce their future effectiveness or trigger adverse reactions. In such cases, recovery depends on the body’s own immune system, which usually takes several weeks. Bacterial conjunctivitis often produces thick yellow or green discharge, while viral conjunctivitis typically causes watery discharge. Using cold compresses and artificial tears can help relieve irritation.

Anti-inflammatory eye drops and ointments
Antibiotic eye ointments or drops can effectively relieve bacterial conjunctivitis.

Cold compress, artificial tear
Cold compresses or artificial tears are recommended. Neurotransmitters respond more quickly to ice than to itchy allergies, reducing itchiness and helping relieve the inflammation and dryness of the eyes caused by conjunctivitis. What’s more, patients should refrain from rubbing their eyes, blowing on them or applying hot compresses, and stop using contact lenses until the symptoms have completely disappeared to avoid further irritation and itching.

Conjunctivitis FAQ
Is conjunctivitis contagious?
Both viral and bacterial conjunctivitis are contagious and can spread from person to person via discharge from the eyes or upper respiratory tract, fingers, clothing and other items such as make-up, towels, etc. Swimmers may also be infected if they swim in contaminated water.
Will conjunctivitis go away on its own?
Bacterial conjunctivitis: it does not heal on its own and requires regular medication such as antibiotic eye ointment or eye drops (prescribed and instructed by an ophthalmologist, not self-purchased).
Viral conjunctivitis does not require special treatment. Most patients recover on their own within 1 to 2 weeks, and adequate rest can help speed up the healing process.
If the condition worsens or complications develop, corneal ulcers may occur, and in severe cases this can even lead to permanent vision loss. Therefore, any eye discomfort should be promptly evaluated and managed by an ophthalmologist.
Can I wear contact lenses when I have conjunctivitis?
Contact lenses should not be worn. They need to be disinfected or replaced with new ones, and should only be used again after full recovery.
How to Prevent Conjunctivitis?
- Avoid touching your eyes. If this cannot be avoided, be sure to wash your hands thoroughly before and after contact.
- Wash hands with liquid soap and water, and rub for at least 20 seconds, or perform hand hygiene with 70% to 80% alcohol-based.
- Do not share personal items, e.g. towels, pillows, eye droppers, eye medicines, eye makeup, contact lenses and other items that may come into contact with your eyes.
- Infected individuals should refrain from work, school or swimming until their symptoms have resolved in order to prevent the spread of infection.

